Multicast Video over IP


 Conventional networking fails to achieve efficiency in the distribution of content.
Point-to-point protocols are not scalable and are unable to broadcast video simultaneously
to large numbers of users.
Conventional networking fails to achieve efficiency in the distribution of content.
Point-to-point protocols are not scalable and are unable to broadcast video simultaneously
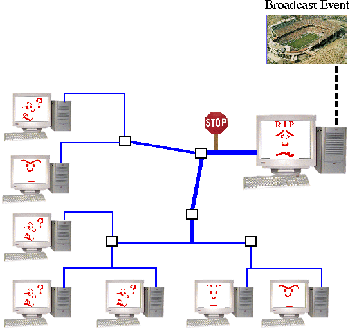
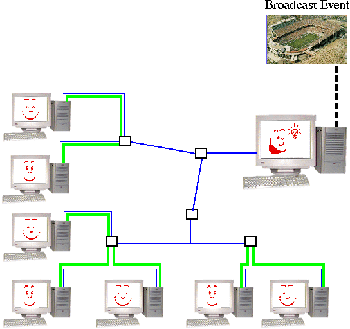
to large numbers of users.However, a system for Scalable Media Delivery (SMD) has been created to allow video to be multicast over several different channels to a large number of users. Clients "tune in" to videos being broadcast. Unlike point-to-point protocols, the video server will have little trouble being able to handle the addition of large numbers of new users tuning in.
Scalable Media Delivery (SMD) uses a powerful set of multicast protocols to reduce network bottlenecks and smooth data flow. Instead of fighting to get the same bits, SMD promotes communcal cooperation through the use of local caches. Every client is also a server that can draw upon an array of distributed network resources. Thus, clients tuning into video can access the video from any number of nearby clients rather than a single server. In addition, error correction is handled locally rather than by a central server which handles all errors throughout the network.


R.G. Kermode, "Smart Network Caches: Localized Content and Application Negotiated Recovery Mechanisms for Multicast Media Distribution", Doctoral Dissertation, MIT Media Lab, June 1998. postscript (2423063 bytes), gzipped postscript (587654 bytes) pdf (1205322 bytes), gzipped pdf (656538 bytes) Abstract
R.G. Kermode, "Scoped Hybrid Automatic Repeat reQuest with
Forward Error Correction (SHARQFEC)," To appear in ACM Sigcomm 98, September 1998, Vancouver, Canada.
gzipped postscript (143524 bytes),
gzipped pdf (126548 bytes)
Preliminary results are available for viewing.
J. Gemmell, E. Schooler, and R. Kermode, "An Architecture for Multicast Telepresentations", To appear: Journal of Computing and Information Technology.
J. Gemmell, E. Schooler, and R. Kermode, "A Scalable Multicast Architecture for One-to-many Telepresentations", IEEE Multimedia Systems 98, June 28 - July 1, 1998, Austin TX, USA